
Made in America
Get Connected With



Email Us
sale@abrvpartsacc.com
Call Us
+1 (626) 448-2100
Made in America
Get Connected With




Installing underground pipes is a critical aspect of various construction and utility projects, ranging from residential drainage systems to extensive municipal waterworks. According to the American Society of Civil Engineers, approximately 30% of all infrastructure failures can be attributed to improper pipe installation, highlighting the need for effective methodologies in this field. The correct installation of underground pipes not only ensures longevity and efficiency but also minimizes the risk of costly repairs and environmental hazards.
A comprehensive approach to installation involves understanding the unique challenges posed by different soil conditions, groundwater levels, and potential environmental factors. Reports by the National Association of Home Builders indicate that more than 50% of homeowners encounter issues related to underground pipes, often stemming from common installation mistakes such as inadequate trenching and failure to account for soil settling. By following best practices and being aware of typical pitfalls, contractors and DIY enthusiasts alike can significantly enhance the reliability of their underground piping systems. This article provides top tips for effective underground pipe installation, aiming to equip readers with the necessary knowledge to undertake successful projects.
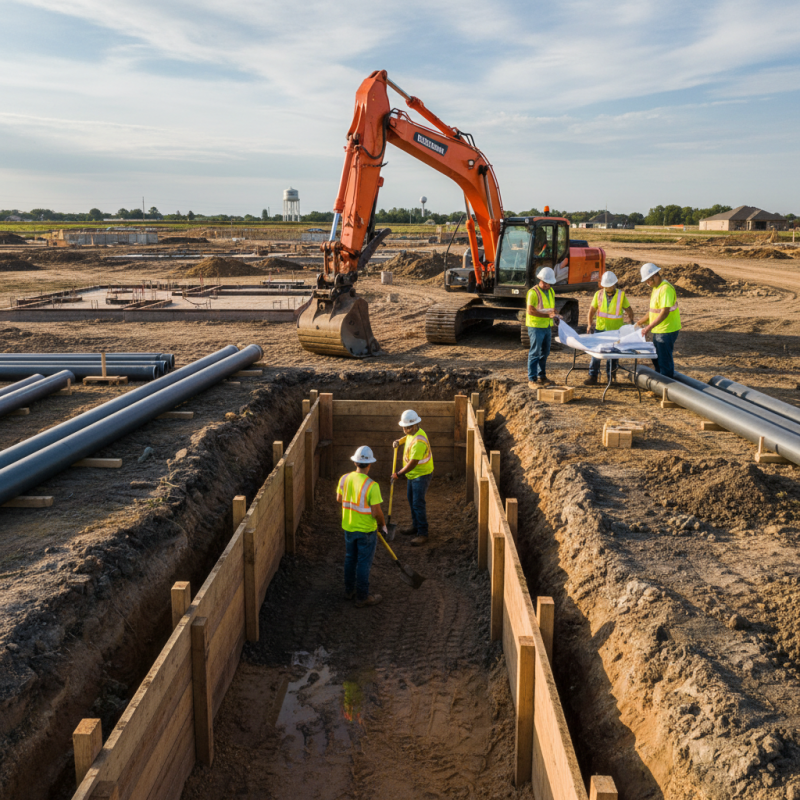

Proper underground pipe installation is crucial for several reasons, making it a fundamental aspect of infrastructure projects. First and foremost, well-installed pipes are essential for the efficient transport of water, sewage, and other fluids, which are vital for both residential and commercial properties. Any flaws in the installation process can lead to leaks, backflow, or even complete system failures, resulting in costly repairs and potential hazards to public health and safety.
Understanding the environmental impact of underground pipe installation reinforces its importance. Improperly laid pipes can disrupt the local ecosystem, leading to soil erosion, water contamination, and damage to plant life. Additionally, considering factors such as soil type, groundwater levels, and potential obstructions is essential for ensuring the long-term viability of an underground system. By prioritizing proper installation techniques and planning, engineers and contractors can safeguard against issues that not only affect individual properties but also the broader community and environment.

Installing underground pipes requires a thoughtful approach to ensure efficiency and durability. One of the essential aspects of the installation process is having the right tools and materials. According to a report from the American Society of Civil Engineers, improper tool selection can lead to significant project delays and increased costs, with up to 30% of labor hours consumed by inefficient practices. Hence, having a checklist of essential tools is vital: a trenching shovel, pipe cutter, and a compactor are indispensable for excavating, cutting, and consolidating the soil around the pipes.
Furthermore, selecting the appropriate pipe material is crucial. Options include PVC, HDPE, and concrete, each with its unique advantages and applications. A study by the Plastics Pipe Institute cites that PVC pipes can have a lifespan of over 100 years when installed properly, making it a popular choice for various underground plumbing projects. Additionally, using joint sealing compounds suited for the selected materials minimizes leakage risks and enhances the overall integrity of the installation. Proper preparation and selection of tools and materials not only streamline the installation process but also significantly improve the system's longevity and reliability.
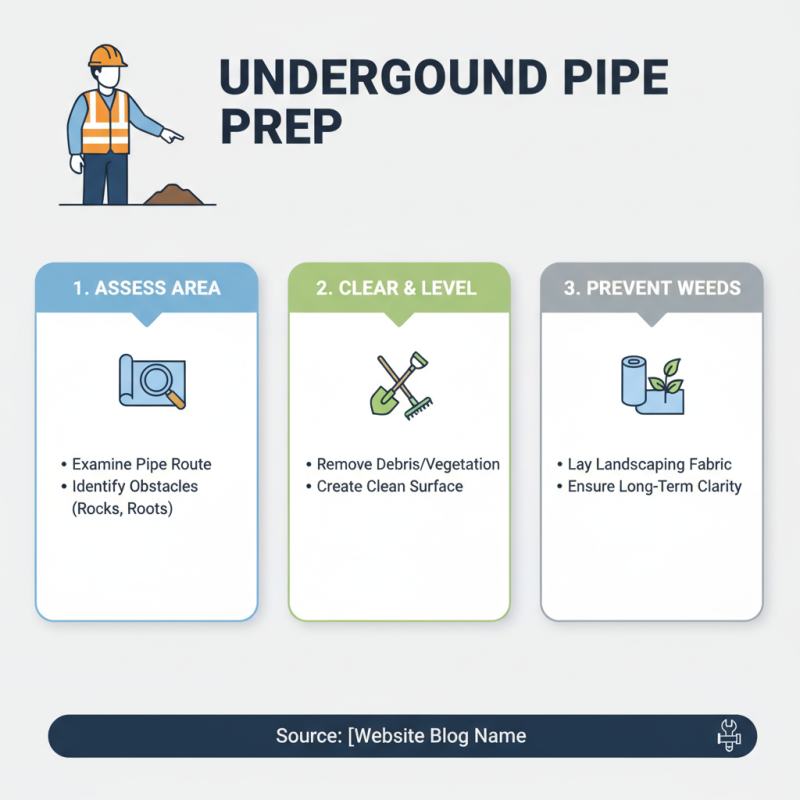
When preparing the site for underground pipe installation, the first crucial step is to assess the area where the pipes will be laid. Begin by clearing the space of any debris, vegetation, or structures that might interfere with the installation process. This includes removing rocks, roots, and other obstacles to create a clean and level surface. Consider using landscaping fabric to prevent future weeds from growing, ensuring that your installation site remains unobstructed in the long term.
Next, it’s important to accurately mark the path of the pipe. Use stakes and string to outline where the pipes will be installed, maintaining a straight line to ensure proper alignment. This marking process will help in calculating the depth needed for the trench and will guide digging efforts. Keep in mind that different types of pipes require varying depths for optimal installation. As you prepare the site, consult local codes and best practices to ensure compliance and safety standards are met. Proper site preparation not only enhances the efficiency of the installation but also reduces the likelihood of costly mistakes down the line.
When installing underground pipes, avoiding common mistakes is crucial for ensuring both the longevity of the infrastructure and the efficiency of your project. One of the most prevalent errors is improper trench preparation. According to industry reports, nearly 30% of pipeline failures originate from inadequate trenching, which can lead to shifting soil and eventual pipe damage. It's essential to assess soil conditions and use appropriate techniques, such as sloping or benching, to prevent collapses that can compromise the installation process.
Another significant mistake often observed during underground pipe installation is the misalignment of pipes. Studies show that aligning pipes inaccurately can result in increased stress on joints and ultimately lead to leaks. Ensuring that pipes are installed at the correct slope and aligned properly is critical. Implementing technology like laser leveling and GPS integration can help mitigate these issues, as these advanced tools provide precise measurements and facilitate better alignment throughout the installation.
Regular inspections and monitoring during installation are also vital to catch any potential errors early. Research indicates that projects with proactive quality control measures reduce the risk of future complications by up to 50%. By focusing on thorough planning and adherence to best practices, you can significantly minimize the risks associated with underground pipe installation.
| Mistake | Impact | Tip to Avoid |
|---|---|---|
| Improper Depth | Can lead to freezing and damage | Follow local codes for depth |
| Wrong Pipe Material | Increased risk of corrosion | Use appropriate materials for soil conditions |
| Poor Bedding | Can cause misalignment and stress | Ensure proper bedding of gravel/sand |
| Neglecting Drainage | Risk of water pooling and damage | Plan for effective drainage systems |
| No Marking or Signage | Increased risk of accidental damage | Clearly mark all underground pipes |
Installing underground pipes requires careful attention to detail to ensure their long-term performance. According to a report by the American Society of Civil Engineers, aging infrastructure has resulted in over 240,000 water main breaks annually in the U.S., often due to poorly installed pipes. Proper installation starts with selecting the right materials and understanding soil conditions. For instance, flexible pipes can better withstand soil movements and pressures, which reduces the risk of failure. Moreover, utilizing proper bedding materials can effectively distribute loads and prevent settlement issues, ensuring that pipes maintain their structural integrity over time.
Another significant factor in ensuring the longevity of underground pipes is avoiding common installation mistakes. A study from the National Research Council highlights that nearly 50% of pipe failures are attributed to inadequate installation practices. This includes improper alignment, insufficient backfill compaction, and neglecting drainage solutions. Installing pipes at the correct depth is also crucial, as it prevents freezing and ensures they are protected from surface loads. Employing modern technologies such as trenchless installation techniques can further enhance the durability of buried pipes by minimizing disruption to the surrounding environment and reducing the risks associated with excavation. Adopting these practices not only promotes long-term performance but also fosters sustainability in pipeline infrastructure.





