
Made in America
Get Connected With



Email Us
sale@abrvpartsacc.com
Call Us
+1 (626) 448-2100
Made in America
Get Connected With




When it comes to plumbing, one of the most critical yet often overlooked aspects is the size of waste pipes. Selecting the ideal waste pipe size can significantly influence the efficiency of your plumbing system. According to renowned plumbing expert, Dr. Emily Thatcher, “The right waste pipe sizes ensure optimal flow and minimize the chances of blockages, which can lead to costly repairs.” Understanding the various waste pipe sizes available is essential for both new constructions and renovations, as it directly impacts how well wastewater is managed in our homes and businesses.
In any plumbing system, proper waste management is key to maintaining hygiene and preventing water damage. A well-chosen waste pipe size not only meets the demands of the household or commercial establishment but also complies with local building codes. Dr. Thatcher emphasizes that, “Selecting the appropriate diameter for waste pipes can be a game-changer in preventing plumbing issues.” Whether you’re a homeowner looking to upgrade your plumbing system or a contractor seeking to ensure compliance with regulations, understanding waste pipe sizes will guide you toward making informed decisions that contribute to a reliable and effective plumbing system.

Waste pipe systems play a crucial role in modern plumbing, ensuring that wastewater is effectively transported away from homes and buildings. Properly designed and maintained waste pipe systems prevent blockages, odors, and potential health hazards, making them essential for a safe and functioning environment. Understanding the size and layout of waste pipes can greatly impact the efficiency of your plumbing system.
When considering the ideal waste pipe size, it’s important to account for factors such as the volume of wastewater generated and the type of fixtures connected to the system. Standard sizes typically range from 1.5 inches for smaller drains, like sinks, to 3 or 4 inches for larger systems, such as those connected to toilets and major appliances. A well-planned layout allows for optimal drainage and minimizes the risk of backflow, ensuring that all wastewater is handled effectively.
Tips: To maintain an efficient waste pipe system, regularly inspect for signs of clogs or leaks. Simple measures, such as using screens over drains to catch debris and scheduling routine cleanings, can extend the life of your plumbing. Additionally, always ensure proper venting in your waste pipe design, as this can significantly improve drainage efficiency and prevent unpleasant odors from seeping into your living space.
This chart displays the recommended drainage capacities for different waste pipe sizes, providing a visual reference for optimal plumbing solutions. Selecting the appropriate waste pipe size is crucial for effective wastewater management in plumbing systems.
When determining the ideal waste pipe size for plumbing needs, several key factors come into play.
One critical consideration is the volume of wastewater
produced by fixtures. A study by the American Society of Plumbing Engineers (ASPE) suggests that
residential bathrooms generate around 20-30 gallons of wastewater per day,
which necessitates proper sizing of the waste pipes to prevent clogs and ensure efficient drainage. Typically,
a 3-inch diameter pipe is recommended for a standard bathroom group, which includes a toilet, sink,
and shower.
Another influencing factor is the length of the piping run. The International Plumbing Code (IPC)
outlines that the longer the distance wastewater must travel, the larger the pipe may need to be to accommodate
flow rates and minimize friction loss. For instance, pipes
that are over 40 feet long may require an increase in diameter to
4 inches to maintain optimal flow characteristics. Additionally, the slope of the waste pipe
plays a significant role, as a ¼ inch per foot slope is generally recommended to facilitate
proper drainage. Understanding these factors ensures that plumbing systems are designed for efficiency and longevity.
When considering the ideal waste pipe size for plumbing needs, standard residential waste pipe sizes play a crucial role in ensuring efficient drainage and preventing blockages. Generally, residential waste pipes come in standardized sizes such as 1.5 inches, 2 inches, and 3 inches in diameter. The 1.5-inch pipes are commonly used for sinks and lavatories, while 2-inch pipes are typically utilized for tub and shower drains. The 3-inch diameter is often reserved for main waste lines where multiple fixtures converge, making it essential for handling a larger volume of waste.
According to industry reports, selecting the appropriate size is vital for maintaining adequate flow rates; a 2-inch pipe can support up to 16 fixture units, whereas a 3-inch pipe can accommodate up to 40 fixture units. This sizing directly impacts the plumbing system's ability to handle wastewater effectively without causing backups or slow drainage. Inadequate pipe sizes can lead to increased pressure and potential failure of the plumbing system, highlighting the importance of adherence to local plumbing codes and professional recommendations when determining the right pipe diameter for specific applications.
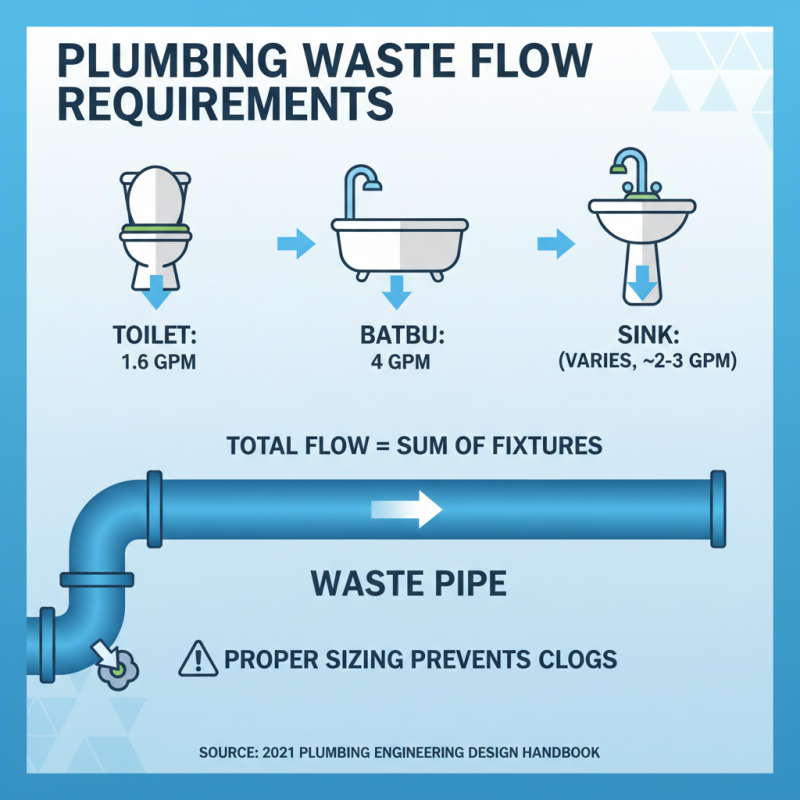
When calculating waste flow requirements for various plumbing fixtures, it's essential to understand how different fixtures impact pipe size and drainage efficiency. Each fixture, whether a sink, toilet, or shower, has its specific flow rate, measured in gallons per minute (GPM). According to the 2021 Plumbing Engineering Design Handbook, a standard toilet typically requires about 1.6 GPM, while a bathtub can demand upwards of 4 GPM during peak use. Consequently, the waste pipes must accommodate these flow rates to prevent clogs and ensure efficient drainage.
To determine the appropriate waste pipe size, one must consider the fixture unit (FU) values assigned to each type of fixture. For instance, a lavatory sink has an FU value of 1, while a kitchen sink carries a value of 2. These values, combined with the total demand of all connected fixtures, guide plumbers in selecting a pipe diameter that can handle the maximum flow without excessive pressure drop. The International Plumbing Code recommends a minimum of a 2-inch diameter for kitchen sinks and toilet connections, ensuring an adequate flow and minimizing potential drainage issues.
Tip: Always factor in the length of the pipe run and any bends or fittings, as these can significantly affect flow capacity. For longer runs, consider increasing the pipe diameter to optimize performance. Additionally, regular maintenance and inspections can help identify potential issues before they escalate, ensuring a smooth operation of your plumbing system.
When it comes to waste pipe sizing, many homeowners and plumbers make critical errors that can lead to significant plumbing issues over time. One common mistake is underestimating the diameter of the waste pipe needed for proper drainage. According to the American Society of Plumbing Engineers (ASPE), a lack of sufficient pipe size can result in slow drainage, increased clogs, and even sewage backups. Standards suggest that kitchen sink waste pipes should ideally be at least 1.5 inches in diameter, while bathroom drains typically require a minimum of 2 inches to accommodate peak flow rates effectively.
Another frequent error involves the incorrect calculation of the total drainage fixture units (DFUs) that a plumbing system will handle. The International Plumbing Code (IPC) recommends considering not just the number of fixtures but also the anticipated usage levels. Failing to accurately assess demands can lead to undersized pipes, which may increase the risk of blockages due to inadequate flow rates. A study published in the Journal of Water Management highlighted that 35% of plumbing failures stem from improper sizing based on miscalculations of DFUs, emphasizing the importance of correct assessments during the design phase.
By being aware of these common pitfalls and adhering to established plumbing codes, one can ensure that waste pipes are always appropriately sized, leading to efficient drainage and long-lasting performance. Engaging with professional plumbing services that understand these standards can also mitigate the risks associated with poor sizing decisions.





